Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept—it’s here, transforming industries, automating tasks, and reshaping decision-making processes in ways that were once unimaginable. From self-driving cars revolutionizing transportation to personalized learning systems enhancing education, AI has become a cornerstone of modern technology. Its applications are vast, touching nearly every aspect of our lives, including healthcare, finance, entertainment, and even our daily routines.
However, as AI continues to advance at an unprecedented pace, it brings with it a host of ethical challenges that demand urgent attention. The rapid integration of AI into society has sparked critical conversations among researchers, policymakers, and business leaders about how to balance innovation with ethical responsibility. While AI holds immense potential to drive progress and improve lives, it also poses significant risks, such as perpetuating bias, compromising data privacy, and displacing jobs.
In this comprehensive article, we explore the ethical considerations of AI across various domains, including work, academics, and daily tasks. Supported by expert insights, real-world examples, and credible research, we aim to shed light on how AI can be harnessed for the greater good while minimizing its potential harms.
1. Ethical AI in the Workplace
AI-driven automation is transforming industries, enhancing efficiency, and streamlining business operations. However, the integration of AI in workplaces also raises ethical concerns regarding employment, privacy, and decision-making fairness.

Workplace Automation and Job Displacement
- AI-powered software is taking over repetitive tasks, reducing the human workload but also raising concerns about job losses.
- Companies like Amazon and Tesla are deploying AI-driven robotics in warehouses and production lines, boosting efficiency but also reducing the demand for human labor in certain roles.
- A 2020 report by the World Economic Forum (WEF) predicts that AI could displace 85 million jobs globally by 2025, while creating 97 million new roles requiring advanced skills (World Economic Forum Report, 2020).
Expert Insight:
“AI will not replace humans, but humans who use AI will replace those who don’t.”
– Kai-Fu Lee, AI investor and former president of Google China.
Bias in AI Hiring Tools
- Many companies use AI-driven hiring platforms to screen candidates, but biased algorithms can lead to discrimination.
- Amazon scrapped its AI recruitment tool after discovering it favored male applicants over female candidates, reflecting biases in historical hiring data.
- Ethical AI requires diverse datasets and continuous monitoring to prevent biased decision-making in employment.
Research Highlight:
A 2021 study by Harvard Business Review found that AI systems trained on biased data can perpetuate gender and racial disparities, highlighting the need for transparency and accountability in AI hiring tools (Harvard Business Review, 2021).
AI and Workplace Privacy
- AI-powered monitoring tools, such as employee tracking software, are raising concerns about surveillance and data privacy.
- A 2022 report by Gartner found that 60% of large employers are using AI to monitor employee performance, sparking debates about the ethical implications of workplace surveillance (Gartner Report, 2022).
Example:
Some companies use AI to analyze employee emails and Slack messages, raising questions about the balance between productivity optimization and respecting employee rights.
2. AI in Academics: Enhancing Learning or Encouraging Cheating?
AI is revolutionizing education by offering personalized learning experiences, automating grading, and enabling students to access vast resources. However, ethical concerns arise in areas such as academic integrity, accessibility, and data privacy.
AI as a Learning Tool
- AI-driven platforms like Duolingo and Coursera personalize learning by adapting to individual student progress.
- AI tutors, such as Google’s Socratic and Khan Academy’s AI assistant, provide instant help, making education more accessible worldwide.
- AI-generated feedback enhances grading efficiency, allowing educators to focus on student development rather than administrative tasks.
Research Highlight:
A 2020 study by McKinsey found that AI-powered tools can improve learning outcomes by 30% when used effectively (McKinsey Study, 2020).
The Ethical Dilemma of AI-Generated Academic Work
- AI writing tools like OpenAI’s ChatGPT can help students generate essays, raising concerns about plagiarism and academic dishonesty.
- Some universities are adopting AI detection tools to identify AI-generated assignments, sparking debates on how to balance AI’s benefits with academic integrity.
Example:
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) has introduced guidelines to teach students how to ethically use AI as an aid rather than a replacement for their own critical thinking.
Privacy and Data Security in Education
- AI collects vast amounts of student data, raising privacy concerns.
- Schools must ensure AI tools comply with data protection regulations like GDPR and FERPA.
Expert Insight:
A 2021 report by UNESCO emphasized the need for ethical AI in education, calling for transparency and accountability in data usage (UNESCO Report, 2021).
3. AI for Simple Tasks: Improving Daily Life While Maintaining Ethics
AI-driven solutions are becoming integral to daily life, assisting in tasks such as shopping recommendations, personal assistants, and even mental health support. However, ethical questions remain regarding over-reliance, misinformation, and data privacy.
AI Assistants and Personalization
- Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant help users set reminders, control smart devices, and answer queries.
- AI-driven recommendation engines, such as those used by Netflix and Spotify, enhance user experience but also raise concerns about data usage and algorithmic manipulation.
Example:
Netflix’s recommendation system uses AI to suggest content, but critics argue it can create echo chambers by limiting exposure to diverse viewpoints.

AI and Misinformation
- AI-generated deepfake videos and misinformation spread easily on social media, influencing public opinion and elections.
- Ethical AI development must prioritize transparency and accountability in information dissemination.
Research Highlight:
A 2023 study by Stanford University found that 67% of deepfake videos are used for malicious purposes, highlighting the need for robust AI regulations (Stanford University Study, 2023).
Mental Health AI and Ethical Challenges
- AI chatbots like Woebot and Replika provide mental health support, but their effectiveness in replacing human therapists is still debated.
- Ethical concerns arise when users develop emotional attachments to AI, potentially impacting their real-life relationships.
Example:
A user of Replika, an AI companion app, reported feeling emotionally dependent on the chatbot, raising questions about the ethical implications of AI in mental health.
4. Addressing AI Bias and Fairness
Bias in AI is a significant ethical issue, as algorithms trained on biased data can reinforce social inequalities.
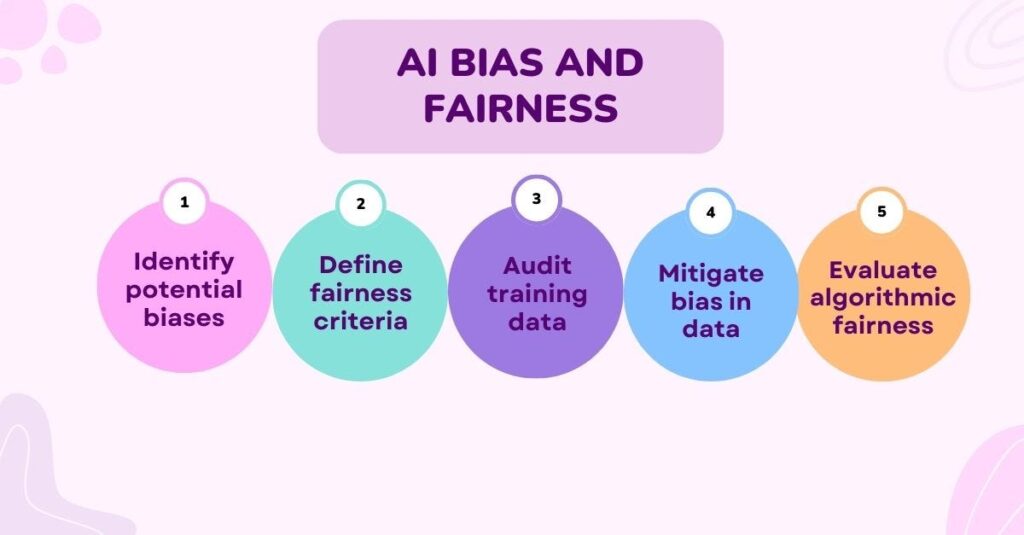
How Bias Enters AI Systems
- AI learns from historical data, which may reflect existing prejudices.
- Example: Facial recognition software often performs poorly on people of color due to biased training datasets.
Efforts to Reduce AI Bias
- Google’s Responsible AI team and IBM’s AI Fairness 360 are developing tools to detect and mitigate bias.
- Organizations must invest in ethical AI development practices and conduct regular audits.
Expert Insight:
“AI should reflect the diversity of the world we live in. If not, we risk perpetuating existing inequalities at an accelerated rate.”
– Timnit Gebru, AI ethics researcher and former Google AI scientist.
5. Legal and Ethical Regulations for AI
As AI continues to expand, governments and regulatory bodies are stepping in to ensure responsible AI usage.

AI Regulations and Policies
- The European Union’s AI Act aims to regulate high-risk AI applications (EU AI Act).
- The United States and China are developing frameworks for AI governance to balance innovation with ethical responsibility.
Corporate Responsibility in AI Development
- Tech giants like Microsoft and OpenAI are advocating for responsible AI development.
- Companies must ensure ethical AI deployment through transparency, accountability, and compliance with legal frameworks.
Example:
Microsoft’s AI Principles emphasize fairness, reliability, and inclusivity in AI development.
Conclusion: The Path Toward Ethical AI
AI’s potential is limitless, but with great power comes great responsibility. Addressing ethical considerations in AI development and implementation is crucial to ensuring fairness, privacy, and accountability.
Key Takeaways:
- AI in workplaces enhances productivity but requires ethical hiring and data privacy considerations.
- AI in education must balance personalization with academic integrity.
- AI-driven personal assistants improve daily tasks but raise concerns about misinformation and over-reliance.
- Bias in AI remains a critical challenge, requiring ongoing mitigation efforts.
- Governments and corporations must collaborate to establish clear AI regulations.
As AI continues to shape the future, ethical considerations must be at the forefront of innovation to ensure AI serves humanity responsibly and fairly.
Join the AI Ethics Conversation
Stay informed about AI developments and ethical considerations by subscribing to AI Review Central. Engage in discussions on how AI can be harnessed responsibly to benefit society as a whole.